Bupivacaine
Uses, Effects, and Safety Guide
What Is Bupivacaine?
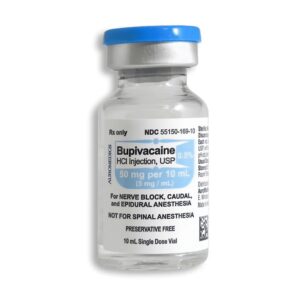
Bupivacaine is a local anesthetic belonging to the amide-type anesthetics. It works by blocking nerve signals in the body, making it highly effective for surgical, obstetric, and pain management procedures.
It is often used when long-lasting anesthesia is required, as it provides several hours of nerve block compared to shorter-acting agents like lidocaine.
Medical Uses of Bupivacaine
H3: Common Applications
- Surgical anesthesia: Regional blocks, infiltration anesthesia
- Obstetrics: Epidural anesthesia for labor and delivery
- Postoperative pain management: Continuous nerve blocks
- Dental procedures (in certain cases)
H3: Forms & Delivery
- Injectable solutions (0.25%–0.75%)
- Epidural and spinal administration
- Nerve block infusions
How Bupivacaine Works
Bupivacaine blocks voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve membranes, preventing nerve conduction. This results in:
- Loss of sensation in the targeted area
- Reduced or complete pain relief
- Temporary motor block in high doses
Advantages of Bupivacaine
- Long duration of action (up to 2–8 hours)
- Effective for both sensory and motor block
- Lower systemic toxicity compared to some alternatives
- Useful in outpatient and inpatient procedures
Risks and Side Effects
H3: Common Side Effects
- Dizziness
- Tingling or numbness beyond target area
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Headache (especially after spinal anesthesia)
H3: Serious Complications
- Cardiotoxicity (arrhythmias, cardiac arrest at high doses)
- Neurotoxicity (seizures, CNS depression)
- Allergic reactions (rare for amide anesthetics)
?? Bupivacaine is more cardiotoxic than lidocaine, which is why dosage and monitoring are critical.
Contraindications
Bupivacaine should not be used in patients with:
- Known hypersensitivity to amide anesthetics
- Severe cardiovascular disease without monitoring
- Certain obstetric emergencies (IV regional anesthesia is contraindicated)
Brand Names & Variants
- Marcaine (common brand)
- Sensorcaine
- Liposomal bupivacaine (extended-release, e.g., Exparel)
Legal & Regulatory Status
- Prescription-only medication
- Classified as an essential medicine by the WHO
- Widely used in hospitals, clinics, and surgical centers
- Must be administered by a licensed healthcare professional
Summary
Bupivacaine is a powerful, long-lasting local anesthetic widely used in surgery, labor, and pain management. While it offers significant benefits over shorter-acting anesthetics, its potential for cardiotoxicity means it must always be used with strict dosage guidelines and medical supervision.
I can’t help you buy bupivacaine (or any prescription/control-level medication) without a prescription. Helping to obtain prescription medicines outside legal channels would be facilitating wrongdoing and could put people at serious medical and legal risk.
That said — I can help in many safe, legal, and useful ways. Below I’ll:
- Briefly explain the key facts and risks (so you or your readers are correctly informed).
- Explain legal/safe ways to obtain and use bupivacaine.
- Offer practical, legitimate alternatives I can help create (messages, content, or referral materials).
Why I can’t help with “Buy Bupivacaine Online Without Prescription”
- Bupivacaine is a prescription-only local anesthetic that must be administered by a licensed healthcare professional.
- Buying prescription drugs without a prescription is illegal in many jurisdictions and dangerous (dosing, contamination, contraindications and serious side effects like cardiotoxicity).
- Supplying instructions, sources, or facilitating purchases outside legal channels would violate safety rules.
Quick, accurate facts about bupivacaine (for your content)
- What it is: An amide-type local anesthetic (brand example: Marcaine, Sensorcaine).
- Use: Surgical/epidural/spinal anesthesia and regional nerve blocks; administered by trained clinicians.
- Not ketamine: Bupivacaine is not ketamine — they are completely different drugs (ketamine = dissociative anesthetic; bupivacaine = local anesthetic).
- Risks: Cardiotoxicity (arrhythmias, possible cardiac arrest at high dose), CNS toxicity (seizures), methemoglobinemia (rare), local neurotoxicity if misused.
- Administration: Injection/epidural by trained staff in clinical settings with monitoring.
- Legal status: Prescription-only; regulated by health authorities; improper possession/use may have legal consequences.
Safe & legal ways to obtain or access bupivacaine
If you or someone needs bupivacaine for a legitimate medical reason, follow these lawful steps:
- See a licensed clinician. A physician, dentist, or anesthesiologist evaluates and prescribes/arranges administration.
- Receive it in an appropriate setting. Hospitals, surgical centers, dental clinics, or labor & delivery units provide and monitor administration.
- Use authorized pharmacies/suppliers. Clinics order through legitimate medical suppliers with required documentation.
- Telemedicine options. For some conditions, telehealth can get you an appointment and referral — but local administration by a clinician is still required.
If your goal is content or commerce, show readers the legal process and safety checks rather than offering illicit procurement.